Status message
Correct! Excellent, you have really done well. Please find additional information below.
Unknown 46 = Fusarium oxysporum complex
Culture: Colonies growing rapidly, 4.5 cm in 4 days, aerial mycelium white, becoming purple, with discrete orange sporodochia present in some strains; reverse hyaline to dark blue or dark purple.

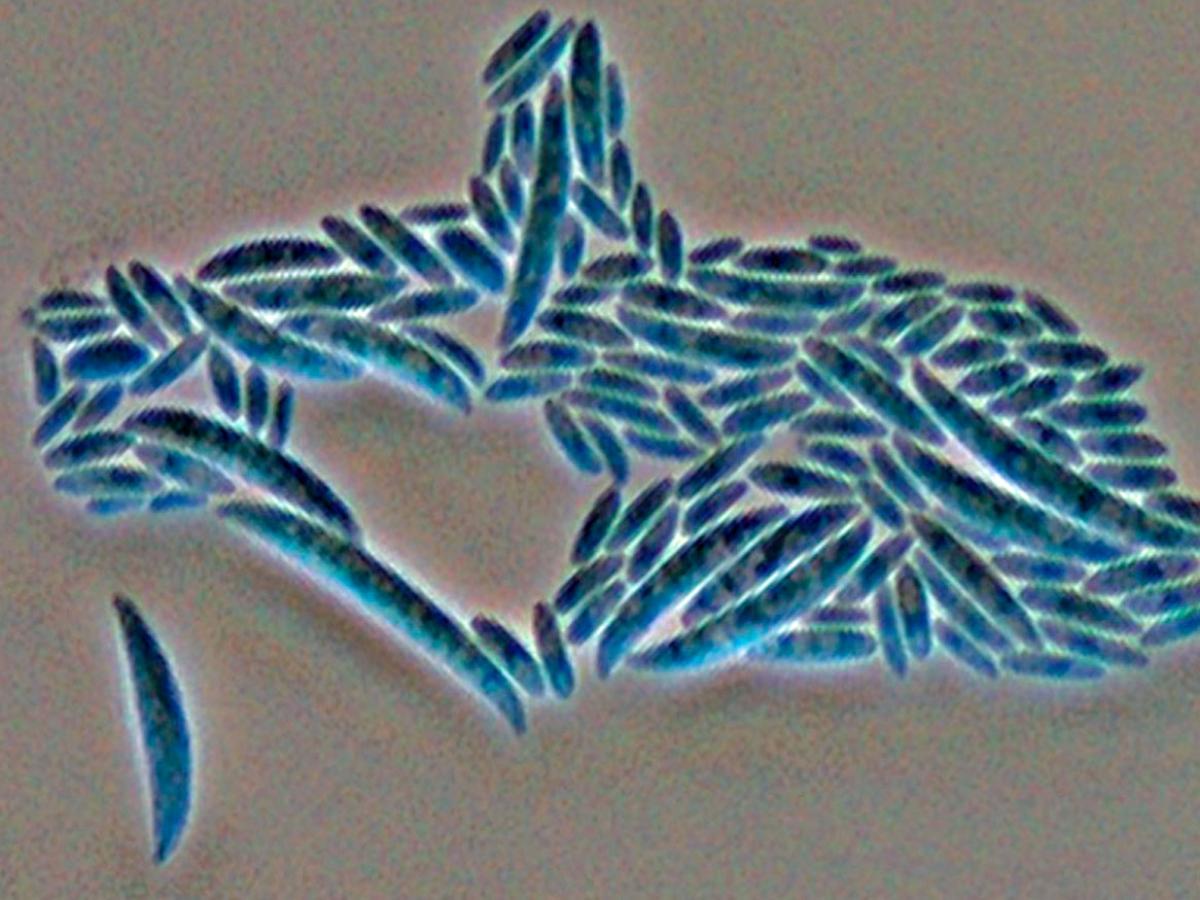
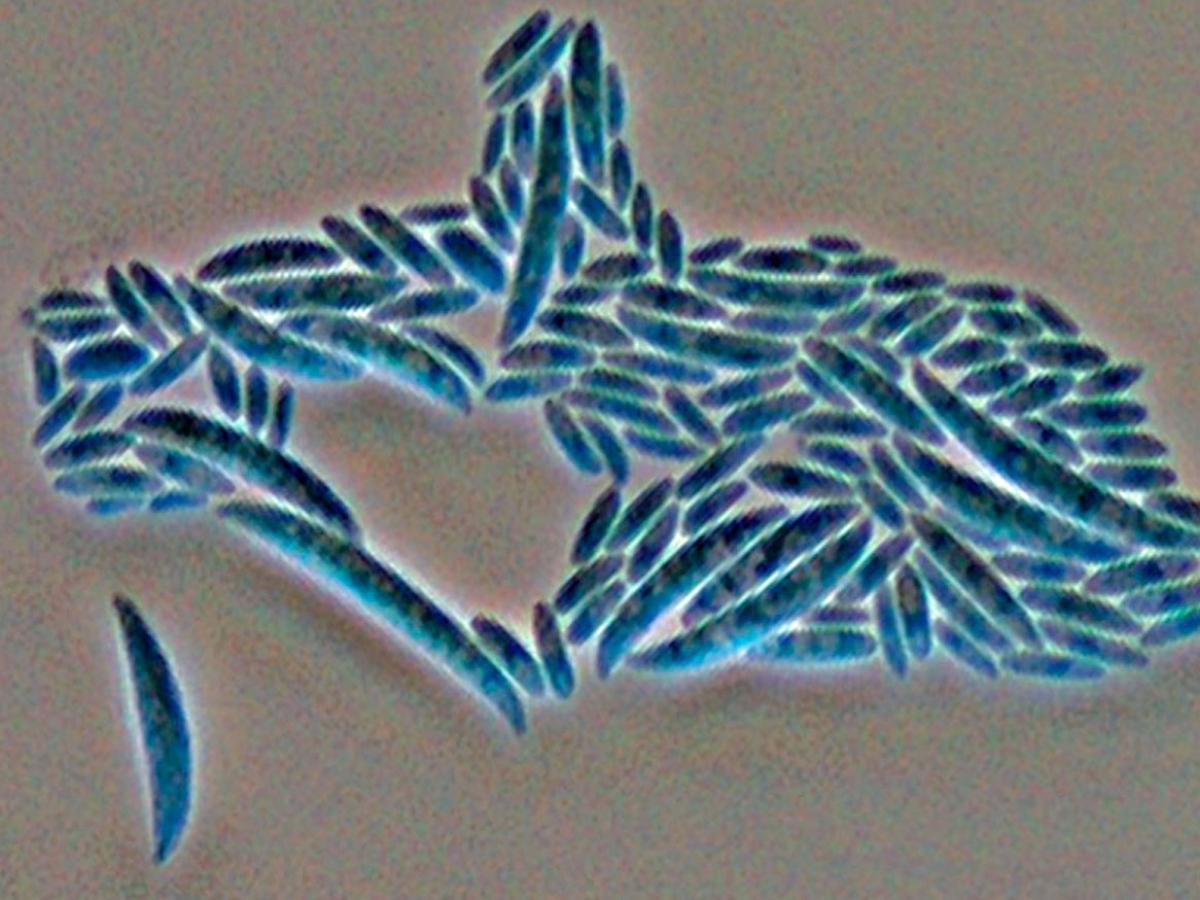
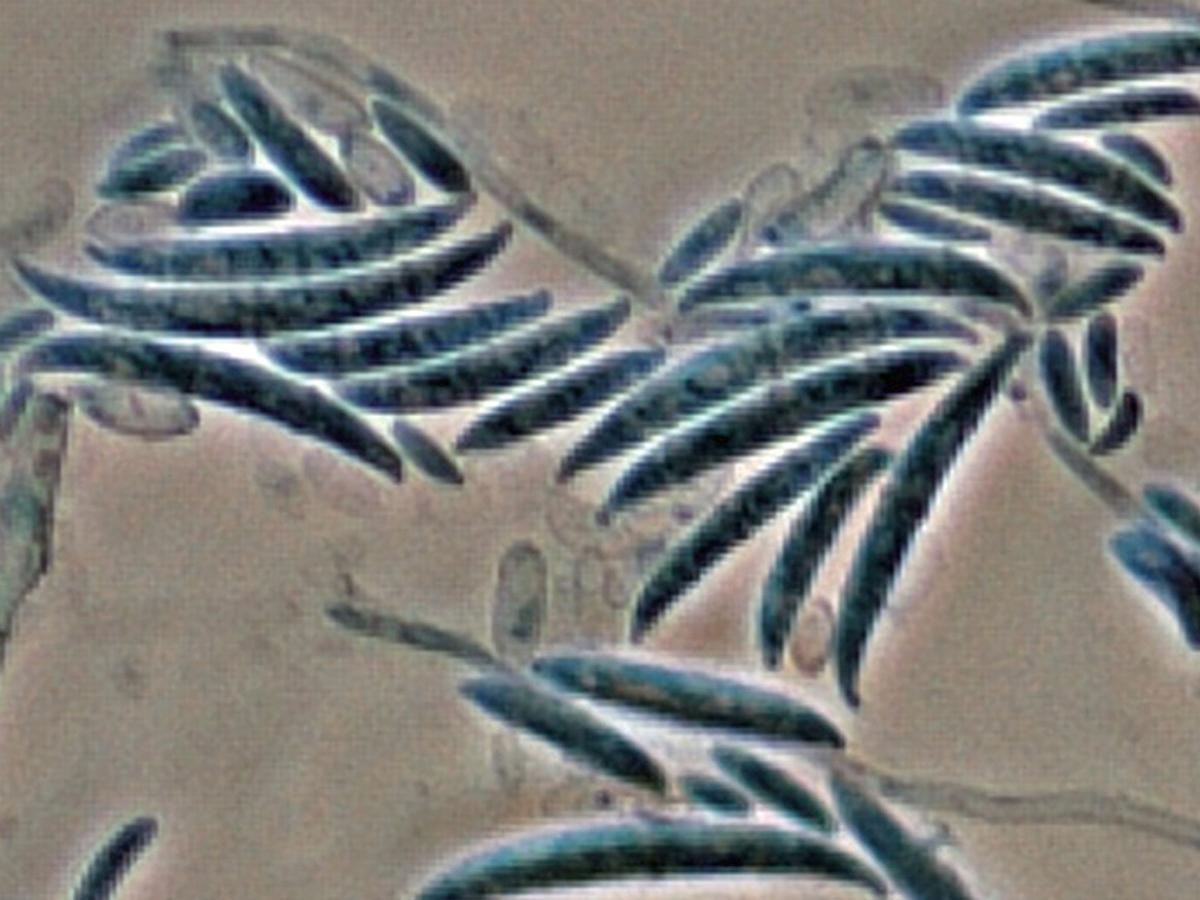
Microscopy: Conidiophores are short, single, lateral monophialides in the aerial mycelium, later arranged in densely branched clusters. Macroconidia are fusiform, slightly curved, pointed at the tip, mostly three septate, basal cells pedicellate, 23-54 x 3-4.5 µm. Microconidia are abundant, never in chains, mostly non-septate, ellipsoidal to cylindrical, straight or often curved, 5-12 x 2.3 - 3.5 µm. Chlamydospores are terminal or intercalary, hyaline, smooth or rough-walled, 5-13 µm. In contrast to F. solani complex the phialides are short and mostly non-septate. RG-2 organism.


Comment: Most Fusarium species are soil fungi and have a worldwide distribution. Some are plant pathogens, causing root and stem rot, vascular wilt or fruit rot. Several species have emerged as important opportunistic pathogens in humans causing hyalohyphomycosis (especially in burn victims and bone marrow transplant patients), mycotic keratitis and onychomycosis. Other species cause storage rot and are important mycotoxin producers.
About Fusarium Back to virtual assessment




