Wound Healing Gel
The wound healing gel uses smart tech with a special ingredient to effectively kill bacteria in hard-to-reach places within wounds, providing excellent antibacterial efficacy whilst preventing side effects.
Dr Richter's team is developing a dual treatment using "DDC-Cu", a patented combination made of diethyldithiocarbamate (DDC) and copper ions (Cu2+). Copper is an essential nutrient of Staphylococci, a group of bacteria commonly found on the skin. While they are usually harmless, they can become problematic in surgical settings as they can cause infections. This group of bacteria can form biofilms, helping them develop resistance to antibiotics over time.
It is hypothesised that DDC-Cu is transported into bacteria through copper uptake mechanisms delivering the DDC-Cu like a Trojan Horse. This smart drug delivery approach will kill antibiotic-resistant bacteria by inhibiting essential copper-dependent food pathways, impairing their ability to survive.
DDC-Cu is not only safe to use and effective against biofilms of antimicrobial-resistant Staphylococci, but it also synergistically enhances antibiotic potency, making resistant bacteria susceptible again to antibiotics.
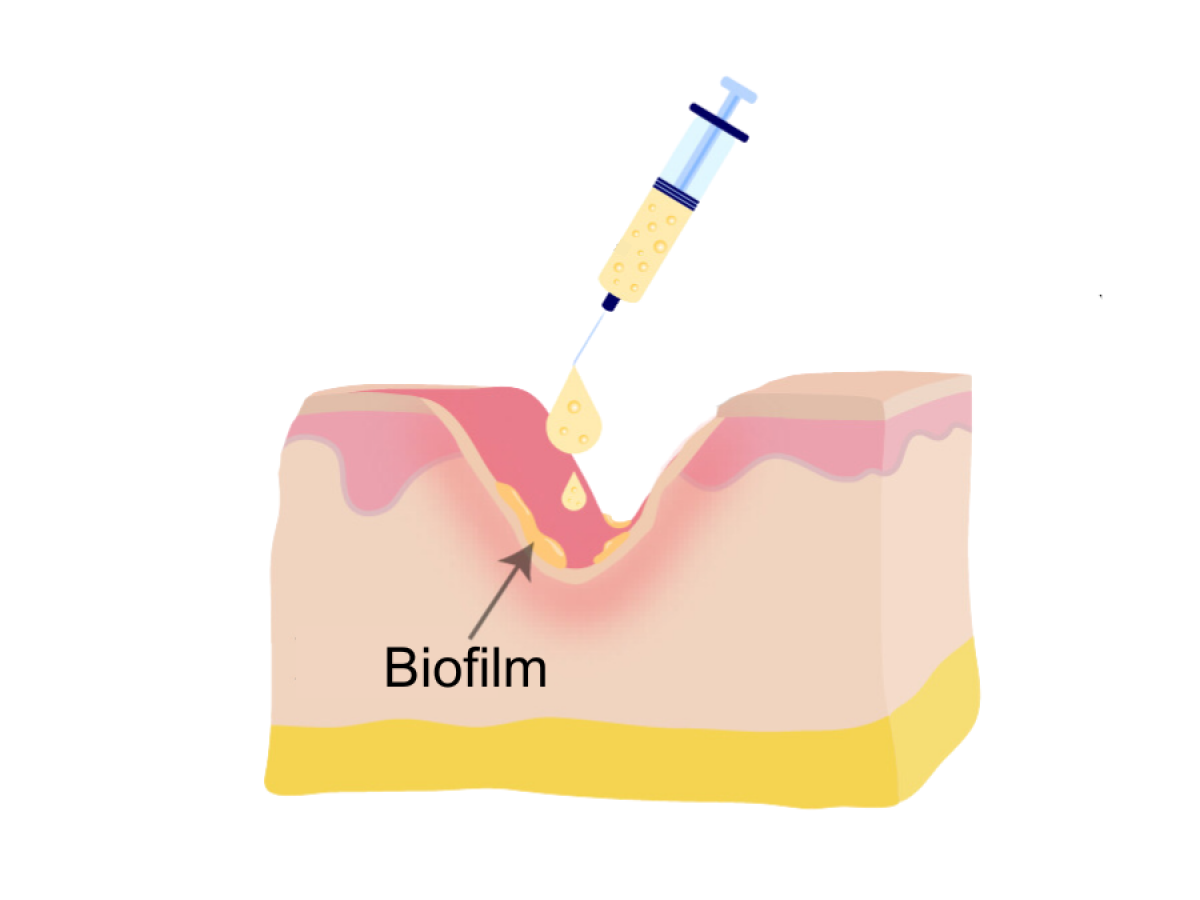
The DDC-Cu Wound Healing Gel is a thermo-sensitive healing gel that reaches bacteria hiding in wound niches.
The smart drug delivery wound healing gel was developed in collaboration with the University of Freiburg to prevent and treat surgical site infections. The gel is liquid at room temperature and can fill uneven niches of wounds where bacteria hide. At body temperature the gel solidifies, locking the drugs in place for the highest localised efficacy against bacteria without causing side effects.
This research is now at the prototype and pre-clinical testing stage.
Team: Dr Adrian Abdo (Post Doc)
In collaboration with Dr Laurine Kaul (Post Doc, Uni of Freiburg), Prof Regine Süss (Uni of Freiburg); Dr Zlatko Kopecki (UniSA); Clinician Prof Guy Maddern (Uni of Adelaide, Queen Elizabeth Hospital)
